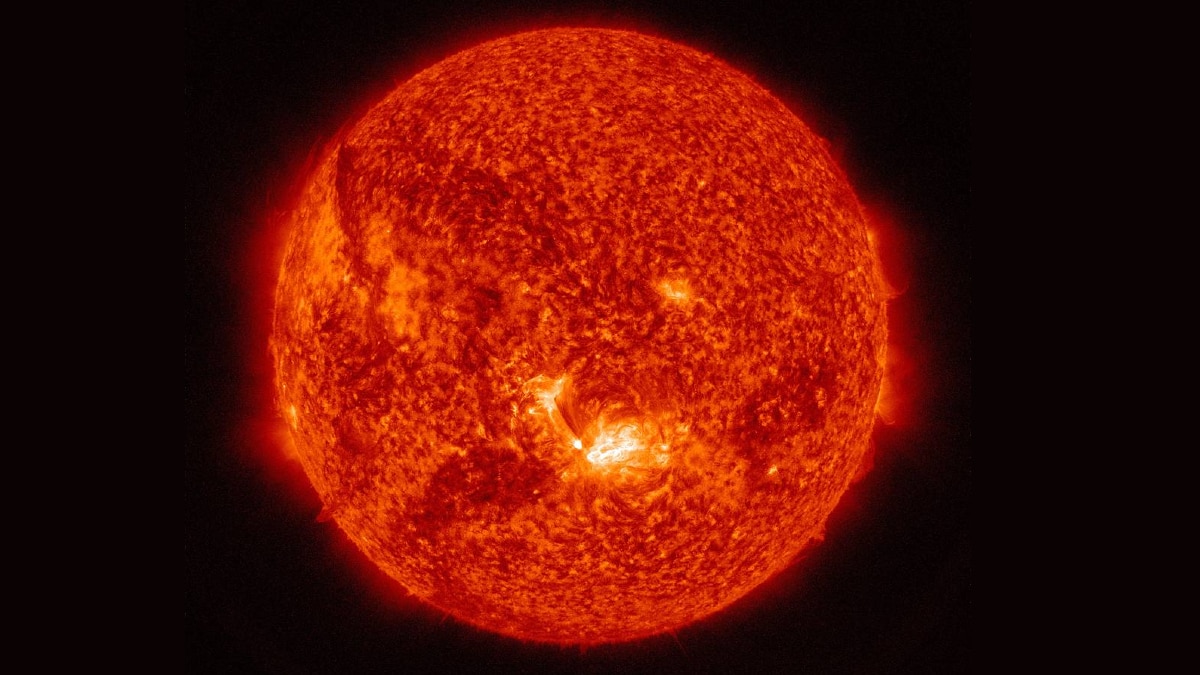
The solar wind is a ubiquitous feature of our solar system. This relentless high-speed flow of charged particles from the sun fills interplanetary space. On Earth, it triggers geomagnetic storms that can disrupt satellites and it causes the dazzling auroras — the northern and southern lights — at high latitudes.
But precisely how the sun generates the solar wind has remained unclear. New observations by the Solar Orbiter spacecraft may provide an answer.
Researchers on Thursday said the spacecraft has detected numerous relatively small jets of charged particles expelled intermittently from the corona — the sun’s outer atmosphere — at supersonic speeds for 20 to 100 seconds.
The jets emanate from structures on the corona called coronal holes where the sun’s magnetic field stretches into space rather than back into the star. They are called “picoflare jets” due to their relatively small size. They arise from areas a few hundred miles wide — tiny when compared to the immense scale of the sun, which has a diameter of 8,65,000 miles (1.4 million km).
“We suggest that these jets could actually be a major source of mass and energy to sustain the solar wind,” said solar physicist Lakshmi Pradeep Chitta of the Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research in Germany, lead author of the research published in the journal Science.
The solar wind consists of plasma — ionized gas, or gas in which the atoms lose their electrons — and is mostly ionized hydrogen.
“Unlike the wind on Earth that circulates the globe, solar wind is ejected outward into interplanetary space,” Chitta said.
“Earth and the other planets in the solar system whiz through the solar wind as they orbit around the sun. Earth’s magnetic field and atmosphere act as shields and protects life by blocking harmful particles and radiation from the sun. But the solar wind continuously propagates outward from the sun and inflates a plasma bubble called the heliosphere that encompasses the planets,” Chitta added.
The heliosphere extends out to about 100 to 120 times further than Earth’s distance to the sun.
The data for the study was obtained last year by one of the three telescopes on an instrument called the Extreme Ultraviolet Imager aboard the Solar Orbiter, a sun-observing probe built by the European Space Agency and the US space agency NASA that was launched in 2020. The Solar Orbiter was about 31 million miles (50 million km) from the sun at the time — about a third of the distance separating the sun and Earth.
“This finding is important as it sheds more light on the physical mechanism of the solar wind generation,” said solar physicist and study co-author Andrei Zhukov of the Royal Observatory of Belgium.
The solar wind’s existence was predicted by American physicist Eugene Parker in the 1950s and was verified in the 1960s.
“Still, the origin of the solar wind remains a longstanding puzzle in astrophysics,” Chitta said. “A key challenge is to identify the dominant physical process that powers the solar wind.”
The Solar Orbiter is discovering new details about the solar wind and is expected to obtain even better data in the coming years using additional instruments and viewing the sun from other angles.
Zhukov said stellar wind is a phenomenon common to most, if not all, stars, though the physical mechanism may differ among various types of stars.
“Our understanding of the sun is much more detailed than the understanding of other stars, due to its proximity and thus the possibility to make more detailed observations,” Zhukov added.
© Thomson Reuters 2023
Check out our Latest News and Follow us at Facebook
Original Source