PORTLAND, USA, Dec 01 (IPS) – Illegal immigration has evolved into a mounting crisis for a growing number of countries worldwide and governments appear to be at a loss on how to deal with the crisis.
Migrant destination countries are facing record high numbers of unlawful border crossings and unauthorized arrivals at their shores, thousands of visa overstayers, and millions of men, women and children residing unlawfully within their countries.
In many of those countries illegal migration is viewed as a threat to national sovereignty. It is seen as undermining cultural integrity. Illegal migration is also creating financial drains on public funds.
Some officials as well as much of the public in those countries have described the continuing illegal immigration to their borders and shores as an “invasion”, a “battle situation” and a “security threat”. And some have called on their governments to “send’em straight back”.
In addition, illegal immigration is also undermining the rule of law, threatening regional cooperation, challenging law enforcement agencies, eroding public support for legal migration, altering political equilibrium and adding to nativism and xenophobia. In addition, the public’s concerns about immigration are reflected in the growing influence of far-right political parties in such countries as Austria, Denmark, Finland, France, Hungary, Italy, Sweden and the United States.
Multinational migrant-smuggling networks are also contributing to the mounting illegal immigration crisis as well as generating substantial profits for criminal organizations. Those networks exploit migrants seeking to leave their countries, offering various services, including transportation, accommodations and critical information.
Government programs and plans to counter migrant smuggling networks have achieved limited success. Also, international attempts to address illegal immigration, such as the Global Compact on International Migration of 2018, have not diminished illegal immigration nor the activities of smuggling networks.
A major factor behind the rise of illegal immigration is the large and growing supply of men, women and children in sending countries who want to migrate to another country and by any means possible, including illegal immigration. The number of people in the world wanting to migrate to another country is estimated at nearly 1.2 billion.
The billion plus people wanting to migrate represents about 15 percent of the world’s population. That number of people wanting to migrate is also more than four times the size of the estimated total number immigrants worldwide in 2020, which was 281 million (Figure 1).
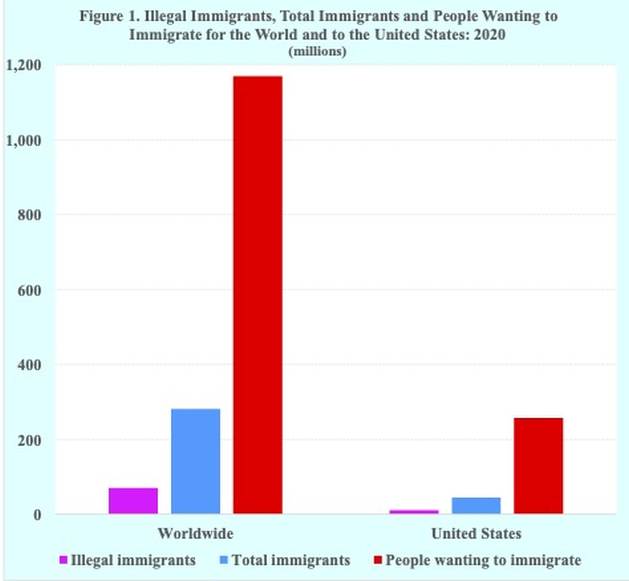
The country with the largest number of immigrants is the United States with almost 48 million foreign-born residents in 2022, or approximately 14 percent of its population. About one quarter of those immigrants, or approximately 11.4 million, are estimated to be illegal immigrants.
While an estimate of the total number of immigrants in the world is readily available, the number of illegal immigrants is a very different matter with few reliable estimates available on a global scale.
Nearly two decades ago it was estimated that perhaps 20 percent of the immigrants were unauthorized migrants. Applying that proportion to the current total number of immigrants of 281 million yields an estimate of about 56 million unauthorized migrants. If the U.S. proportion of illegal immigrants is applied to the total global immigrant population, the resulting estimated number of illegal immigrants in the world is approximately 70 million.
The widely recognized human rights regarding international migration are relatively straightforward. Articles 13 and 14 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights respectively state, “Everyone has the right to leave any country, including his own, and to return to his country”, and “Everyone has the right to seek and to enjoy in other countries asylum from persecution”.
Importantly, however, everyone does not have the right to enter nor remain in another country. The unlawful entry into a country and overstaying a temporary visit are clearly not recognized human rights. Moreover, to be granted asylum, an individual needs to meet the internationally recognized definition of a refugee.
According to the United Nations 1951 Refugee Convention and the 1967 Protocol, a refugee is a person who is unable or unwilling to return to his or her home country due to past persecution or a well-founded fear of being persecuted in the future “on account of race, religion, nationality, membership in a particular social group, or political opinion.”
Difficult living conditions, such as unemployment, poverty, inadequate housing, lack of health care, marital discord and political unrest, do not qualify an individual for the internationally recognized refugee status nor to a legitimate claim for asylum.
Nevertheless, in the absence of a right to migrate to another country, people wanting to do so are increasingly turning to illegal immigration. And upon arriving at the destination country, many are claiming the right to seek asylum.
Once inside the country, the legal determination of an asylum claim often takes years, permitting claimants time to establish households, find employment and integrate into accepting communities, such as sanctuary cities. Also, many of the unauthorized migrants believe, based on the experiences of millions before them, that government authorities will not repatriate them even if their asylum claim is rejected, which is typically the case.
The mounting illegal immigration crisis is complicated by 103 million people who are estimated to have been forcibly displaced worldwide by mid-2022. That number is a record high for forcibly displaced people and is expected to grow in the coming years.
Approximately 50 percent of those forcibly displaced were displaced internally and 5 percent were people in need of international protection. In addition, the number of refugees has reached a record high of nearly 33 million worldwide and the estimate for asylum seekers is close to 5 million (Figure 2).
The worldwide numbers of forcibly displaced people, internally displaced people and refugees have increased substantially since the start of the 21st century. For example, over the past two decades the numbers of displaced people increased from 38 million to nearly 86 million (Figure 3).
Many of those people have been displaced by weather-related events. UNHCR estimates that an annual average of nearly 22 million people have been forcibly displaced by events related to weather, such as wildfires, floods, and extreme heat temperatures.
Moreover, the numbers of displaced people are expected to increase substantially over the coming decades. Some estimate that by midcentury more than one billion people, largely from less developed countries, could be displaced due to climate and environmental changes and civil unrest.
By third decade of the 21st century, the following major trends contributing to the mounting global illegal migration crisis have become abundantly clear:
- Powerful forces worldwide are fueling illegal immigration, including demographics, poverty, smuggling networks, civil unrest and increasingly climate change, which is creating “climate refugees”.
- Those potent forces are resulting in large and increasing numbers of men, women and even unaccompanied children arriving at borders and landing on shores of destination countries without authorization.
- Unauthorized migrants, as well as visa overstayers, seek to settle in those destination countries by any means available and are not prepared to return to their countries of origin.
- Most of the large and growing numbers of unauthorized migrants now residing unlawfully within countries are not likely to be repatriated.
Finally, it is also clear that neither governments nor international agencies have yet been able to come up with effective policies and programs to address the mounting global illegal immigration crisis.
Joseph Chamie is an independent consulting demographer, a former director of the United Nations Population Division and author of numerous publications on population issues, including his recent book, “Births, Deaths, Migrations and Other Important Population Matters.”
© Inter Press Service (2022) — All Rights ReservedOriginal source: Inter Press Service
Check out our Latest News and Follow us at Facebook
Original Source