Kashmir’s Apple Industry Faces Dire Threats as Climate Change Takes its Toll — Global Issues
SHOPIAN, INDIA, Nov 02 (IPS) – Of Kashmir’s seven million inhabitants, a staggering one million rely directly on apple farming. The region is pivotal in India’s apple and horticulture production, contributing to over 70 percent of the country’s apple supply. This not only provides income to farmers but also sustains a vast network of laborers, traders, and transporters within the fruit economy.
However, this year paints a grim picture for the apple industry. Drastic fluctuations in weather patterns, including unseasonal rainfall and unexpected temperature surges, have left apple farmers in a state of deep concern and distress.
In the southern region of Shopian, renowned for its high-quality apple exports, farmers lament the sharp decline in production, considering this trend as a severe threat to their livelihoods.
Perturbed Orchardists
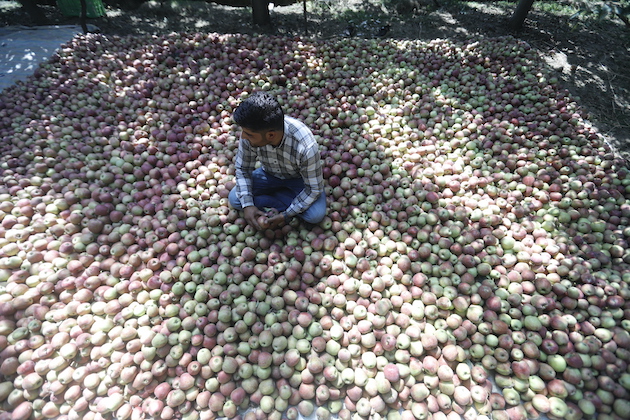
Abdul Karim Mir is one such farmer from the area. His apple orchard is spread over three acres. This year, his produce dipped drastically due to the late arrival of summer and a sudden increase in temperatures when autumn was nearing. “There are scores of apple growers like me who used to be excited about the harvest as it would provide us with immense profits and wider appreciation. The Kashmiri apples are world-famous. There are few pesticides and chemical sprays used for their growth. They are extremely delicious and nutritious. But now, the tale seems different,” Mir told IPS.
He says last year, his orchard produced more than 500 boxes of apples. However, this year, says Mir, the count is not more than 300.
“This is because the bloom at the onset of spring didn’t happen on time. The temperatures were not more than 10 degrees when they should have been more than 20. And at the end of the summer, which is the month of August and September, the temperatures surged suddenly. This had a direct impact on the crop. The productivity plummeted, and so did our hopes of a profitable harvest,” Mir said.
Ghulam Rasool Bhat, another apple farmer from central Kashmir’s Ganderbal, says the situation for the apple growers due to climate change in Kashmir is becoming dismal.
“I estimate around 50 percent of loss this year. Even when we are plucking the fruit from the trees, the loss is of such a magnitude. Now imagine, when we load them in trucks for export, how much more produce will be lost during the transition period,” Bhat said.
He adds that though the government has launched a few schemes for apple growers that include subsidized fertilizers and facilitation of storage, climate change is leaving production in tatters.
Bhat says the cold wave grips Kashmir valley in the months of May and June; otherwise, the summer months when fruits normally grow in the region are fine. “Then, in the first week of September, Kashmir recorded the hottest day of summer. The temperatures were recorded at 34.2°C. Such scorching heat was last recorded 53 years ago. This is unprecedented. It damaged the apple crop beyond repair,” he added.
Horticulture is considered the backbone of Kashmir’s economy, and there are an estimated 144,825 hectares of land dedicated to apple-growing in the region. The industry annually produces 1.7 million tons of apples, and their exports have been valued at INR 6000 crore (USD 826,860,000).
Heat Wave Wreaks Havoc
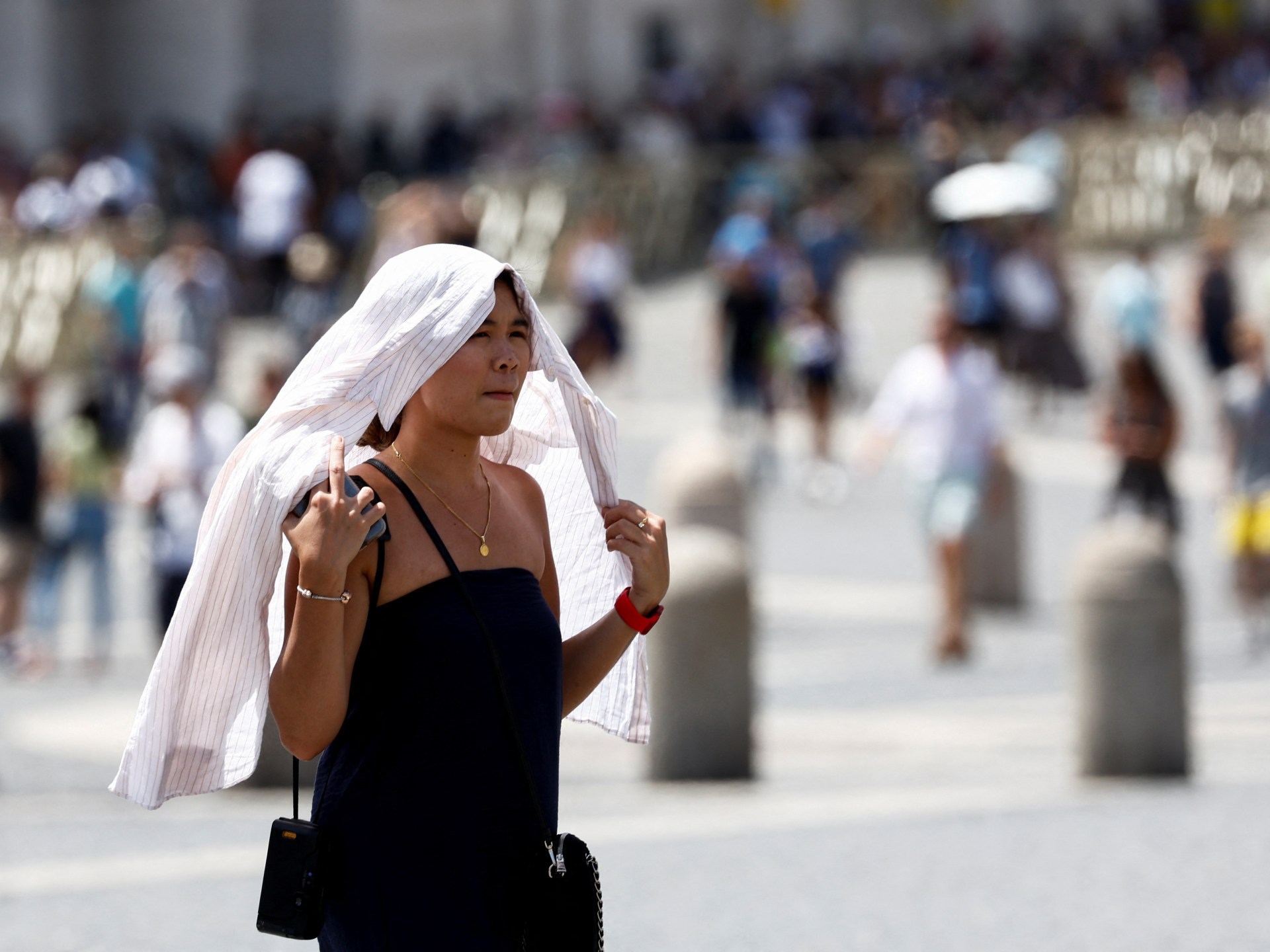
Apart from India, the relentless grip of global heat waves has unleashed a series of environmental crises across the globe. Canada and Hawaii have experienced intensified wildfires, while South America, Japan, Europe, and the United States have been subjected to extreme heat waves.
According to the American space agency NASA, our planet has witnessed the hottest June to August period on record this year. It marked the hottest summer ever recorded in the Northern Hemisphere, contrasting with the warmest winter in the Southern Hemisphere.
NASA’s data reveals that the months of June, July, and August were a staggering 0.23 degrees Celsius warmer than any previous summer in their records and a scorching 1.2 degrees Celsius warmer than the average summer temperatures observed between 1951 and 1980.
These alarming trends have been attributed to the emission of greenhouse gases, which stand as a significant driver behind climate change and the global warming phenomenon responsible for the extreme conditions we witnessed during this sweltering summer.
In the year 2016, India’s northern state of Rajasthan experienced an unprecedented heatwave, with temperatures soaring to a staggering 51 degrees Celsius in the scorching month of May, breaking all previous records. Tragically, this extreme heatwave claimed the lives of an estimated 1,000 people in the state due to dehydration and hyperthermia. In the same year, the southern states of India also withstood the worst of the relentless heatwave, resulting in the tragic loss of 800 lives.
At the UN Climate Change Conference (COP24) in December 2015, a report from the World Health Organization (WHO) emphasized the urgent need for India to address climate change. The report highlighted that both India and China stand to gain substantial health benefits from tackling climate change, with potential gains estimated at a remarkable USD3.28-8.4 trillion for India alone.
Furthermore, the report revealed that the value of health improvements resulting from climate action would be twice the cost of global mitigation policies. This benefit-to-cost ratio is even more favorable for countries like China and India.
Government data indicates that the persistent drought and rising temperatures have adversely affected more than 330 million people in India. Research conducted by the Joint Global Change Research Institute and Battelle Memorial Institute, Pacific Northwest Division, underscores that climate change will disproportionately impact the country’s marginalized communities. These communities, often lacking financial resources and adequate education, rely on agriculture for their sustenance and livelihood. Under the looming threat of climate change, their options are severely limited, leading to increased vulnerability.
The research also warns that in a country prone to natural disasters, the well-being of those affected, particularly those with limited means to recover, will become a significant factor under climate change. This could potentially lead to political instability, strain public budgets, and foster social unrest.
IPS UN Bureau Report
Follow @IPSNewsUNBureau
Follow IPS News UN Bureau on Instagram
© Inter Press Service (2023) — All Rights ReservedOriginal source: Inter Press Service
Check out our Latest News and Follow us at Facebook
Original Source