Food Insecurity Fears as Pakistan Faces Cyclone, Monsoon Season — Global Issues
PESHAWAR, Jun 13 (IPS) – A warning by the UN that Pakistan may face acute food insecurity in the coming months should serve as a wake-up call for the government to focus on the flood-hit areas where the people still live without shelter, medication, and proper food, analysts say.
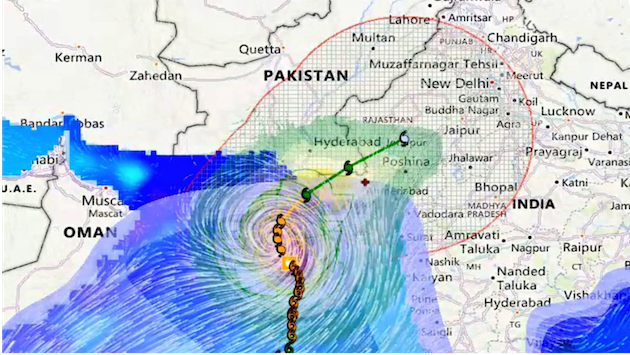
The warning comes as the National Forecasting Centre in Islamabad warned of an extremely severe cyclonic storm Biparjoy that is expected to make landfall in the country in the coming days.
A mass evacuation of about 80,000 people from its path in Sindh province and India’s Gujarat state is underway in areas where severe storms and high winds are expected.
Ahead of the storm and the expected monsoon season, a recent United Nations report warned that acute food insecurity in Pakistan is likely to be further exacerbated in coming months if the economic and political crisis further worsens, compounding the effects of the 2022 floods – which the country is yet to recover from.
The report titled “Hunger Hotspots” was jointly published by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Food Programme (WFP), is a stark reminder to the government, which is yet to cater to the needs of the population hit by severe floods in June-July last year. The two UN agencies have further warned that acute food insecurity will likely deteriorate further in 81 hunger spots — comprising 22 countries, including Pakistan, during the outlook period from June to November 2023.
According to the report, Pakistan, the Central African Republic, Ethiopia, Kenya, Congo, and Syria are hotspots with great concern, and the warning is also extended to Myanmar.
Pakistan’s Federal Minister for National Food Security and Research, Tariq Bashir Cheema, disputed the report regarding possible “acute food insecurity” in Pakistan and termed it “an effort to spread sensationalism and declare the country a hunger hotspot like African countries.”
He alleged that the two UN agencies wanted to declare Pakistan a “hotspot” for famine like African countries.
“Pakistan had a bumper wheat crop this year, and 28.5 million tonnes of wheat production had been recorded, along with the carry-over stock of the previous year,” he told IPS.
However, analysts and NGOs working in the field said the report was accurate and urged the government to take strong measures for food security before the new wave of flooding.
Almost one year after unprecedented floods ravaged Pakistan, more than 10 million people living in flood-affected areas remain deprived of safe drinking water, leaving families with no alternative to use potentially disease-ridden water, Muhammad Zaheer, an economist, told IPS.
In January, donors pledged more than USD10.7 billion for Pakistan’s flood-stricken population in Geneva against an estimated USD16.3 billion recovery bill.
“All the amount pledged at the conference are loans which will be sent to the government from time to time. However, the flood-stricken people are yet to benefit,” he said.
Zaheer said that affected people in Sindh, Balochistan, and parts of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa need support due to the fear of more rains.
According to the report, over 8.5 million people were likely to experience high levels of acute food insecurity.
The situation has been compounded by last year’s floods which caused damage and economic losses of Rs30bn to the agriculture sector.
According to the UN Development Programme (UNDP), a?Post-Disaster Needs Assessment?(PDNA) estimated flood damages to exceed USD 14.9 billion, economic losses over USD 15.2 billion, and reconstruction need over $16.3 billion.
The food insecurity and malnutrition situation will likely worsen in the outlook period, as economic and political crises are reducing households’ purchasing power and ability to buy food and other essential goods, it notes.
A UNICEF report said that an estimated 20.6 million people, including 9.6 million children, need humanitarian assistance in hard-hit districts with high malnutrition, poor access to water and sanitation, and low school enrollment.
“Frail, hungry children are fighting a losing battle against severe acute malnutrition, diarrhea, malaria, dengue fever, typhoid, acute respiratory infections, and painful skin conditions. As well as physical ailments, the longer the crisis continues, the greater the risk to children’s mental health,” it said.
UNICEF will continue to respond to urgent humanitarian needs while also restoring and rehabilitating existing health, water, sanitation, and education facilities for families returning home. An estimated 3.5 million children, especially girls, are at high risk of permanently dropping out of school.
“But much more support is needed to ensure we can reach all families displaced by floods and help them overcome this climate disaster. It will take months, if not years, for families to recover from the sheer scale of the devastation,” it said.
The floods affected 33 million people, while more than 1,700 lives were lost, and more than 2.2 million houses were damaged or destroyed. The floods damaged most of the water systems in affected areas, forcing more than 5.4 million people, including 2.5 million children, to rely solely on contaminated water from ponds and wells.
Sultana Bibi, who lost her home and a few cattle in the flood in Swat district, said there was no government assistance so far.
“We have received some foodstuff from the local NGO in the early days, but we need financial assistance to rebuild our homes. Many people still live with their relatives,” Bibi, 50, told IPS.
Representatives of Al-Khidmat Foundation, a national NGO, which is on the ground in Swat and other areas to help the people, said the situation is yet to improve.
“Unsafe water and poor sanitation are key underlying causes of malnutrition. The associated diseases, such as diarrhea, prevent children from getting the vital nutrients they need. Malnourished children are also more susceptible to waterborne diseases due to already weakened immune systems, which perpetuates a vicious cycle of malnutrition and infection,” he said.
“We fear more flood as June has begun. Last year, we faced severe floods during this month. The government is required to help the people,” analyst Abdul Hakim said.
Hakim, a university lecturer in environmental sciences in Swat district, told IPS that the people would be worst-hit in case of floods this year, and the people haven’t recovered from the last year’s devastating rainwaters.
Pakistan Medical Association’s Dr Abdul Ghafoor said that people still rely on medical camps organized by NGOs as health facilities destroyed by floods haven’t been operational.
“We want the government to take the FAO/WFP report seriously and safeguard the affected people against water and food-borne ailments,” he told IPS.
IPS UN Bureau Report
Follow @IPSNewsUNBureau
Follow IPS News UN Bureau on Instagram
© Inter Press Service (2023) — All Rights ReservedOriginal source: Inter Press Service
Check out our Latest News and Follow us at Facebook
Original Source






