‘Catastrophic’ hunger recorded in Haiti recorded for first time, UN warns — Global Issues
Hunger has reached a catastrophic level – the highest level 5, on the Integrated Food Security Phase Classification index, or IPC) – in the capital’s Cité Soleil neighbourhood.
According to the latest IPC analysis, a record 4.7 million people are currently facing acute hunger (IPC 3 and above), including 1.8 million people in Emergency phase (IPC 4) and, for the first time ever in Haiti, 19,000 people are in Catastrophe phase, phase 5.
Currently, 65 percent of Cité Soleil’s population, especially the poorest and most vulnerable, are in high levels of food insecurity with 5 percent of them in urgent need of humanitarian assistance.
Increased violence, with armed groups vying for control of the vast and now lawless area of Port-au-Prince, has meant that residents have lost access to their work, markets and health and nutrition services. Many have been forced to flee or just hide indoors.
Rural insecurity
Food security has also continued to deteriorate in rural areas, with several going from Crisis to Emergency levels.
Harvest losses due to below average rainfall and the 2021 earthquake that devastated parts of the Grand´Anse, Nippes and Sud departments, are among the other devastating factors, beyond the political and economic crisis.
“WFP stands with the people of Haiti – serving the vulnerable and helping the poorest. We are here to ensure schoolchildren get a nutritious meal each day, families meet their basic food needs and communities are empowered,” said Jean-Martin Bauer, WFP Country Director in Haiti.
‘Time of tumult’
“This is a time of tumult in Haiti. But there is a way forward. We all need to be steadfast and focus on delivering urgent humanitarian assistance and supporting long-term development.”
“We need to help Haitians produce better, more nutritious food to safeguard their livelihoods and their futures, especially in the context of a worsening food crisis,” said José Luis Fernández Filgueiras, FAO Representative in Haiti. “Resource mobilization efforts must be scaled up in order to strengthen the resilience of households targeted by emergency food assistance to increase their self-reliance.”
For years, natural hazards and political turmoil have taken a toll on Haitians who were already in need in both rural and urban areas. The onset of the global food crisis, with rising food and fuel prices, has led to growing civil unrest that has plunged Haiti into chaos, completely paralyzing economic activities and transport.
The basic food basket is out of reach for many Haitians. Inflation stands at a staggering 33 percent and the cost of petrol has doubled.
UNDP Haiti/Borja Lopetegui Gonzalez
Port-au-Prince, Haiti’s capital.
Delivering solutions
Despite the volatile security situation in the capital, Port-au-Prince, WFP provided more than 100,000 people with emergency assistance in the metropolitan area in 2022. WFP’s focus remains on strengthening national social protection and food systems that are central to the country’s recovery efforts and long-term development.
Over the next six months, WFP requires US$ 105 million for crisis response and to tackle root causes and bolster the resilience of Haitian.
FAO has been providing emergency livelihoods support to small-scale vulnerable farming households. During the autumn agricultural season starting this month, FAO aims to reach close to 70,000 people with cash for work, food crop production assistance, goat and poultry breeding assistance, and food storage and processing support for school feeding programmes. FAO urgently requires some $33 million to assist more than 470,000 of the most vulnerable people.
While the agencies continue operating in Haiti as the security situation allows, increased insecurity, violence and lack of fuel are hampering humanitarian operations which are critical for the most vulnerable Haitians.
Cholera, near ‘death sentence’
And, nearly 100,000 children under the age of five who are already suffering from severe acute malnutrition -also known as severe wasting – are especially vulnerable to the ongoing cholera outbreak affecting Haiti, UNICEF has warned.
At a time when much of the country is facing growing food insecurity, acutely malnourished children have weakened immune systems and they are at least three times more likely to die if they contract cholera, further reinforcing the need for urgent action to contain the disease.
Since cholera was first reported on 2 October 2022, there have been 357 suspected cases with more than half of these in children under 14.
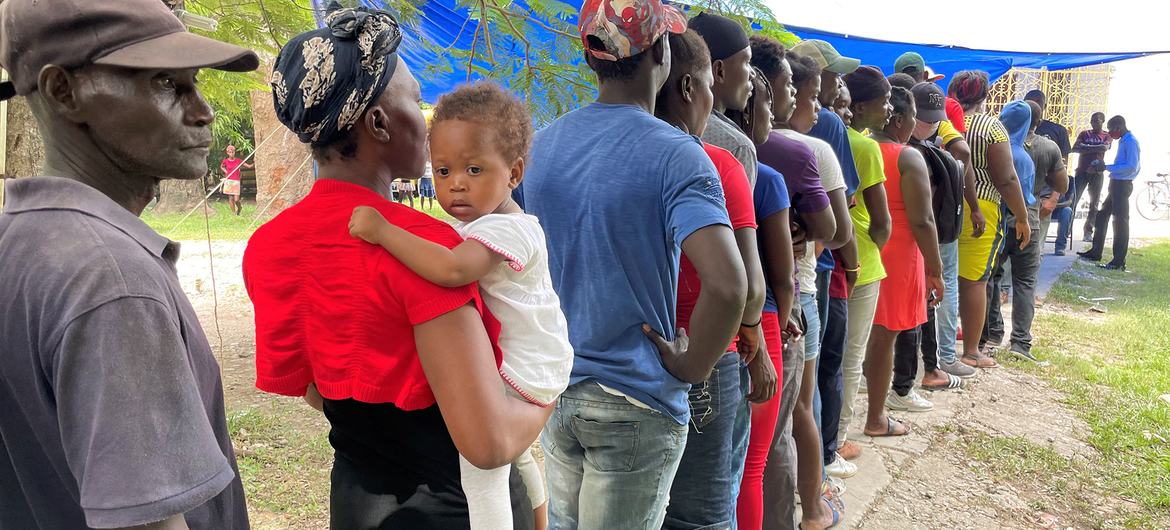

© UNICEF/Jonathan Crickx
People queue to receive hygiene kits in Les Cayes, southwest of Haiti.
Children aged between one and four years are at the greatest risk.
“The crisis in Haiti is increasingly a children’s crisis,” said Bruno Maes, UNICEF Representative in Haiti. “One in three of those suffering from cholera is under the age of five.
“For children who are already weak from a lack of nutritious food, catching cholera, and suffering the effects, including diarrhoea and vomiting, is close to a death sentence. They must be identified and treated urgently, and concrete measures must be taken to prevent new cholera cases in the communities.”
In Cité Soleil, where the first cholera case was reported, up to 8,000 under-fives are at risk of dying of concurrent malnutrition, wasting in this case, and cholera unless urgent action is taken to contain this threat.
Health system decimated
The health system has been brought to its knees in Haiti following the gang blockade of the country’s principal fuel terminal.
Around three-quarters of major hospitals across the country, which rely on diesel generators for electricity, report being unable to provide regular services. Fuel shortages also mean there are now only three ambulances functioning in Port-au-Prince – with close to none running across the rest of the country.
Vulnerable populations, including pregnant women and girls, are the most impacted by restricted access to health services.
UNFPA, the UN’s sexual and reproductive health agency, estimates that close to 30,000 pregnant women are at risk of being unable to access essential healthcare, and almost 10,000 could experience life-threatening – if not fatal – obstetric complications without skilled medical assistance. Around 7,000 survivors of sexual violence could be left without medical and psychosocial support by the end of the year.
Aid for displaced
“Despite the extremely challenging security situation and fuel shortages, UNFPA and our partners are operating mobile clinics frequently in internally displaced persons sites around Port-au-Prince,” said Saïdou Kaboré, UNFPA Representative in Haiti.
“Our trained community workers are doing all they can to ensure that women and girls, especially pregnant women and survivors of violence, can access services and support that are critical to their health and survival.”
Check out our Latest News and Follow us at Facebook
Original Source