Caring for Water Where Mining Leads to Wealth and Tragedies in Brazil — Global Issues
BELO HORIZONTE/ITABIRITO, Brazil, May 19 (IPS) – The southeastern Brazilian state of Minas Gerais owes its name to the main economic activity throughout its history: mining – of gold since the 17th century and later iron ore, which took on an industrial scale with massive exports in the 20th century.
The so-called Iron Quadrangle, a mountainous area of some 7,000 square kilometers in the center of the state, concentrates the state’s minerals and mining activity, long questioned by environmentalists, who have been impotent in the face of the industry’s economic clout.
But the threat of water shortages in Greater Belo Horizonte, population six million, along with two horrific mining accidents, reduced the disparity of forces between the two sides. Now environmentalists can refer to actual statistics and events, not just ecological arguments.
Belo Horizonte, the capital of the state, experienced an unprecedented water crisis in 2014 and 2015, during a drought that affected the entire southeast of Brazil.
“For the first time we experienced shortages here that only the semi-arid north of the state was familiar with,” said Marcelo da Fonseca, general director of the Mining Institute of Water Management (Igam).
On Jan. 25, 2019, a tailings dam broke in Brumadinho, 35 kilometers from Belo Horizonte as the crow flies. The tragedy killed 270 people and toxic sludge contaminated more than 300 kilometers of the Paraopeba River, which provided 15 percent of the water for the Greater Belo Horizonte region (known as RMBH), whose supply has not yet recovered.
On Nov. 5, 2015, a similar accident had claimed 19 lives in Mariana, 75 kilometers from Belo Horizonte, and silted up more than 600 kilometers of the Doce River on its way to the Atlantic Ocean. (The river, whose waters run eastward, do not supply the RMBH.)

Mining hazards
Minas Gerais has more than 700 mining tailings dams. The latest data from the State Environmental Foundation (Feam) show 33 in different degrees of emergency, four of which are at level three – high risk and mandatory evacuation of endangered residents – and nine at level 2 – recommended evacuation.
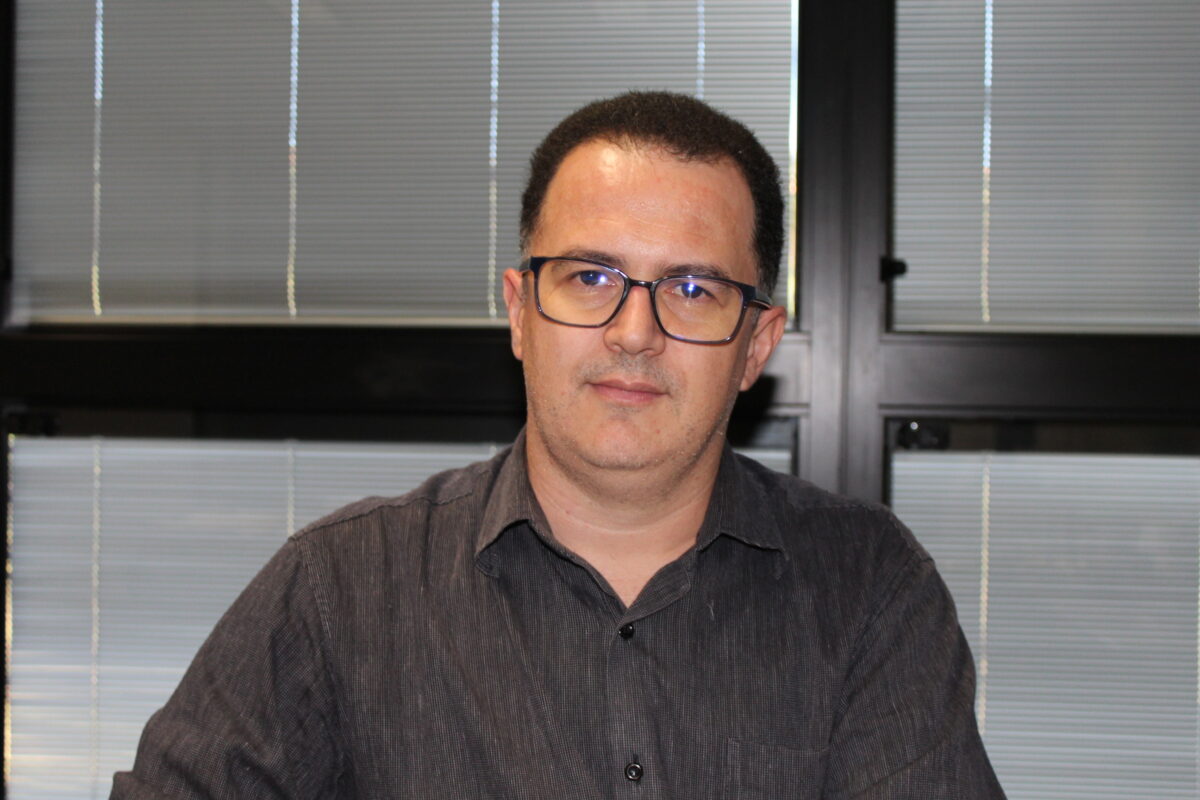
“We are hostages of the mining companies, they occupy the territory and make other economies unviable,” said Camila Alterthum, one of the founders and coordinators of the Cresce Institute and an activist with the Fechos, Eu Cuido movement, promoted by the Rio de las Velhas Watershed Committee.
Fechos is the name of an Ecological Station, a 603-hectare integral conservation area belonging to the municipality of Nova Lima, but bordering Belo Horizonte.
“There are mountains here that recharge the Cauê aquifer, which supplies more than 200,000 inhabitants of southern Belo Horizonte and a neighborhood in Nova Lima,” an adjoining municipality, said Alterthum, who lives in Vale do Sol, a neighborhood adjacent to Fechos.
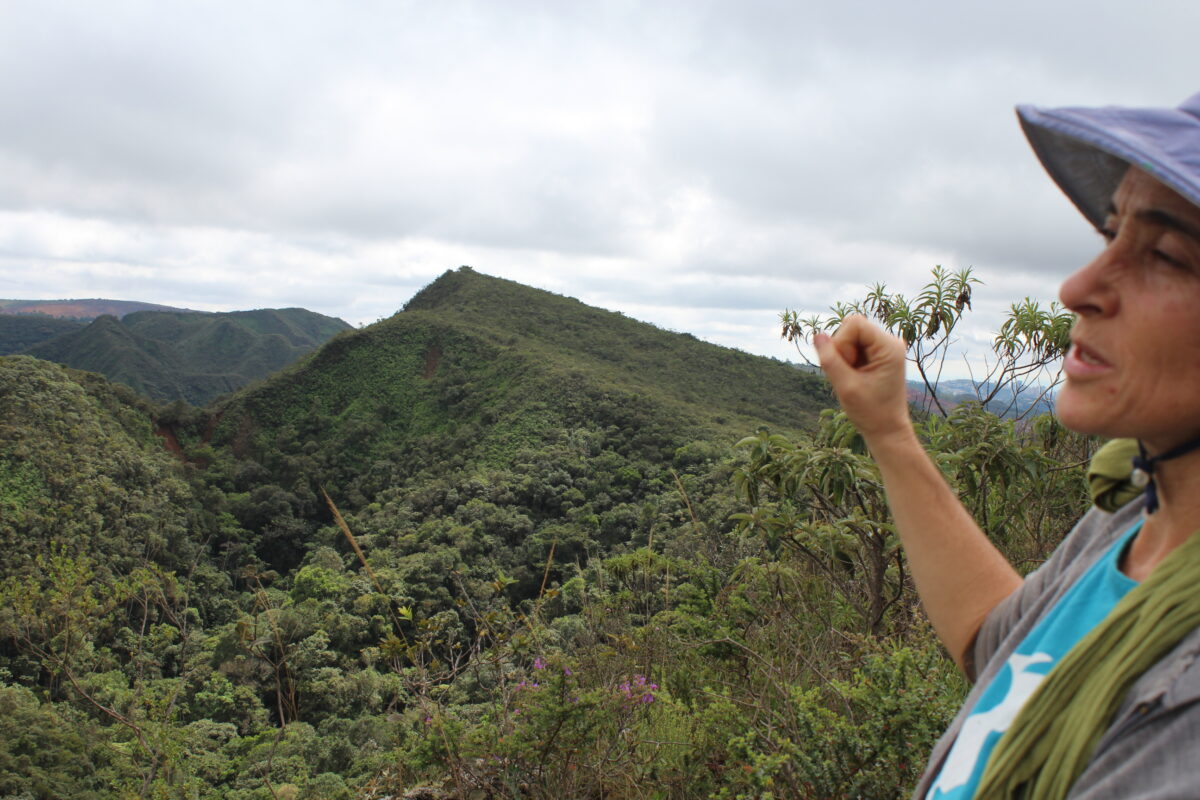

Her movement presented to the Minas Gerais state legislature a bill to expand Fechos by 222 hectares, to provide more water and preserve local biodiversity.
But Vale, Brazil’s largest mining company, aims to expand its two local mines in that area.
In order to acquire the land, it is offering double the number of hectares for conservation, a counterproposal rejected by the movement because it would not meet the environmental objectives and most of it is an area that the company must preserve by law anyway.
A fiercer battle was unleashed by the decision of the Minas Gerais government’s State Environmental Policy Council, which has a majority of business and government representatives, to approve on Apr. 30 a project by the Taquaril company to extract iron ore from the Curral mountain range.
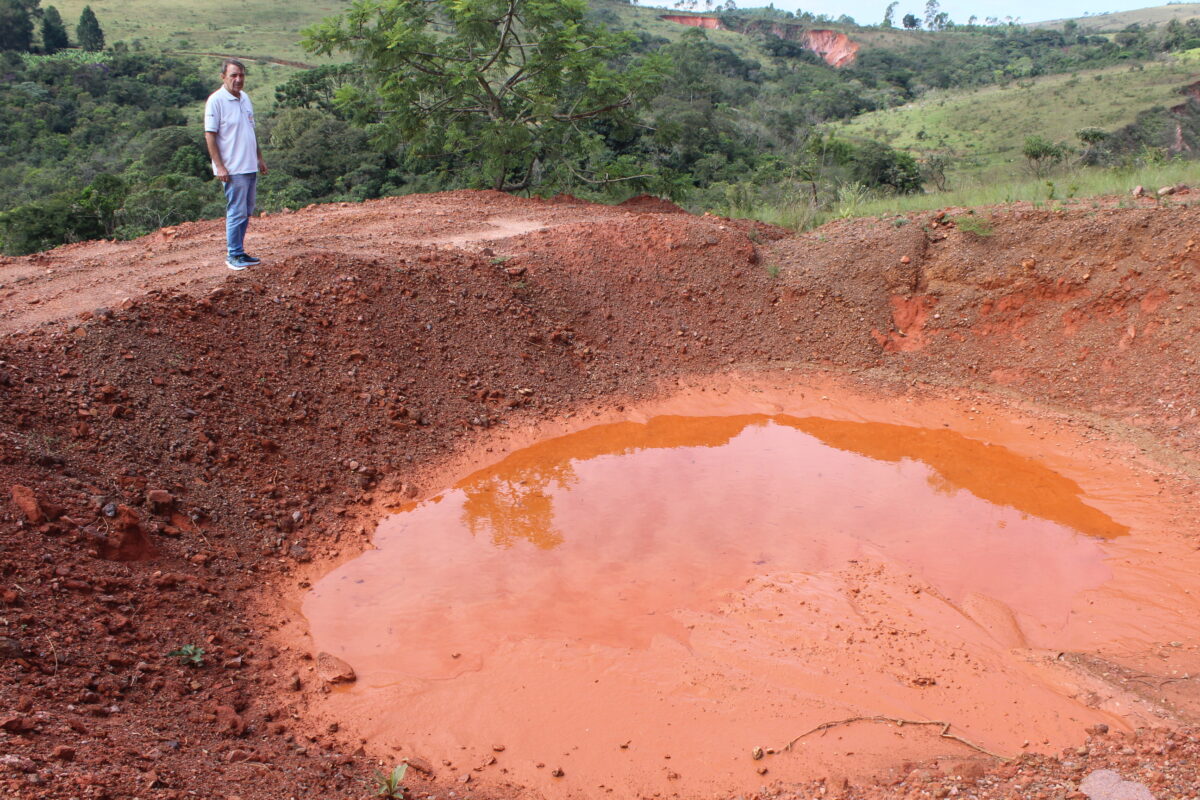

This mountain range is the most prominent landscape feature of Belo Horizonte, in addition to being important in terms of water and environmental aspects for the capital, although it is located on its border, on the side of the municipality of Nova Lima. The mining threat triggered a huge outcry from environmentalists, artists and society in general.
Droughts and erosion
There are other threats to the RMBH’s water supply. “We are very close to the springs, so we depend on the rains that fall here,” Fonseca told IPS at Igam headquarters in Belo Horizonte.
Two consecutive years of drought have seriously jeopardized the water supply.
Two basins supply the six million inhabitants of the 34 municipalities making up Greater Belo Horizonte.
The Velhas River accounts for 49 percent of the water supply and the Paraopeba River for 51 percent, according to Sergio Neves, superintendent of the Metropolitan Business Unit of the Minas Gerais Sanitation Company (Copasa), which serves most of the state.
The Paraopeba River stopped supplying water after the 2019 accident, but its basin has two important reservoirs in the tributaries. The one on the Manso River, for example, supplies 34 percent of the RMBH.
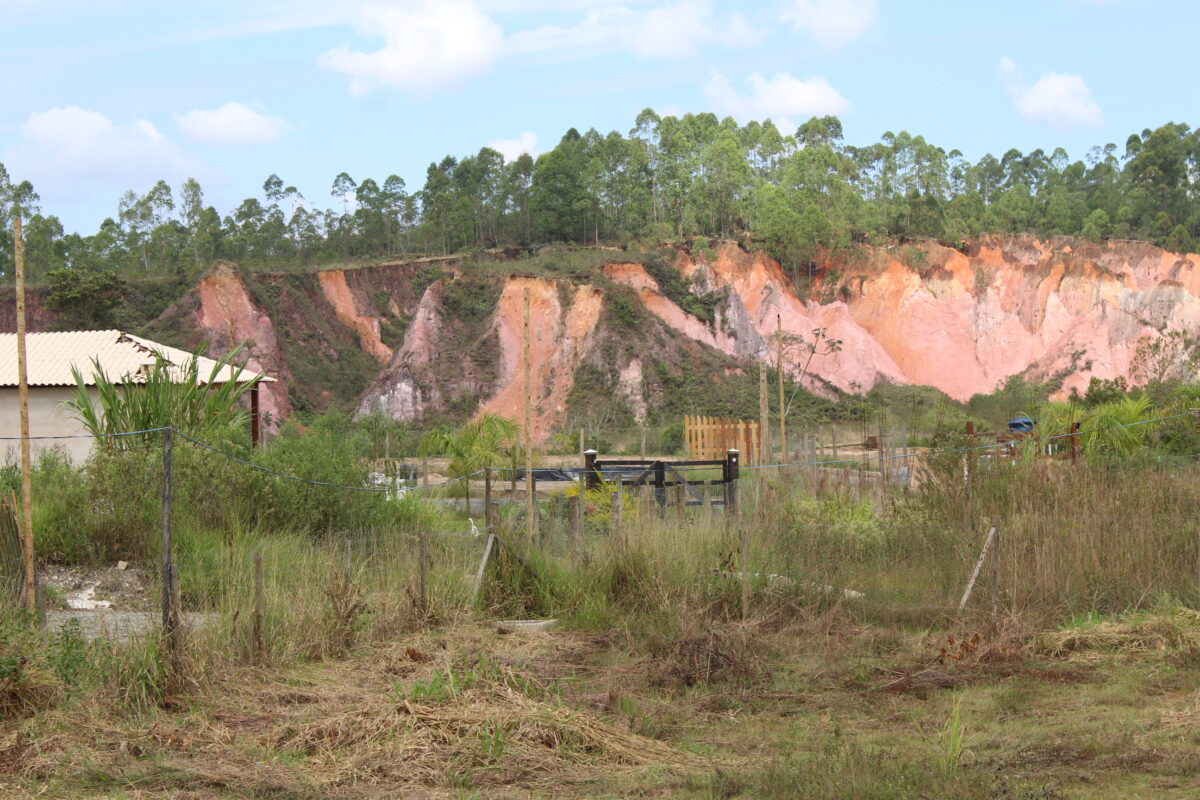

The Velhas River only has a small hydroelectric power plant reservoir, with a capacity of 9.28 megawatts, but it is generating only four megawatts. It is run-of-river, that is, it does not store enough water to regulate the flow or compensate for low water levels.
In addition, sedimentation has greatly reduced its storage capacity since it began to operate in 1907. The soil upstream is vulnerable to erosion and has been affected by urban and agricultural expansion, local roads and various types of mining, not only of iron ore, which aggravate the sedimentation of the rivers, said Fonseca.
Decentralized solutions
The municipal government of Itabirito, which shares the headwaters of the Velhas basin with Ouro Preto, the gold capital in the 18th century, is promoting several actions mentioned by Fonseca to mitigate erosion and feed the aquifers that sustain the flow of the rivers.

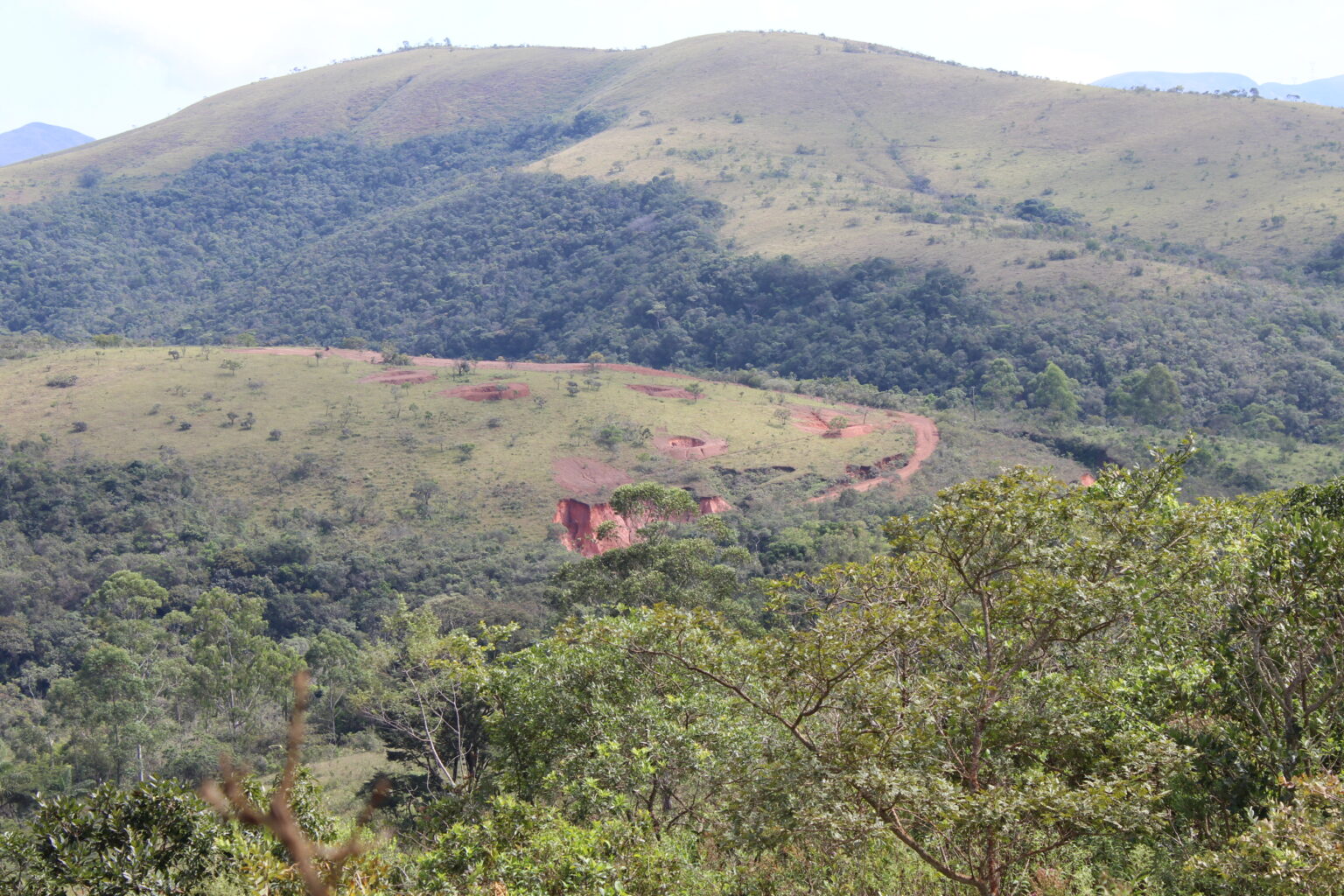
It is intriguing to see craters in some rural properties in Itabirito, especially on hills or gently sloping land.
They are “barraginhas”, explained Julio Carvalho, a forestry engineer and employee of the Municipal Secretariat of Environment and Sustainable Development. They are micro-dams, holes dug to slow down the runoff of rainwater that causes erosion.
This system prevents a large part of the sediment from flowing into the rivers, as well as the phenomenon of “voçorocas” (gullies, in Portuguese), products of intense erosion that abound in several parts of Itabirito and Ouro Preto, municipalities where the first tributaries of the Velhas are born.
As these are generally private lands, the municipal government obtains financing to evaluate the properties, design the interventions and put them out to bid, in agreement with the committees that oversee the watersheds, Carvalho told IPS.

For country roads, which generate a great deal of erosion in the undulating topography, “dry boxes” are used, as well as small holes in the banks to retain the torrents or at least curb their speed, he said.
Other “mechanical land use and conservation practices” include recovering water sources through reforestation and fencing to prevent animals from invading water sources and trampling the surrounding areas.
Itabirito is also seeking to dredge the river of the same name, which crosses the city, to reduce sedimentation, which was aggravated by flooding in January, when the water level in the river rose unusually high.
Environmental education, a program of payments for environmental services and the expansion of conservation areas, in the city as well, are the plans implemented by Felipe Leite, secretary of environment and sustainable development of Itabirito since 2019.
“We want to create a culture of environmental preservation,” partly because “Itabirito is the water tank of Belo Horizonte,” he told IPS.
The municipal government chose to cooperate with the mining industry, especially with the Ferro Puro company, which decided to pave a road and reforest it with flowers as part of a tourism project.
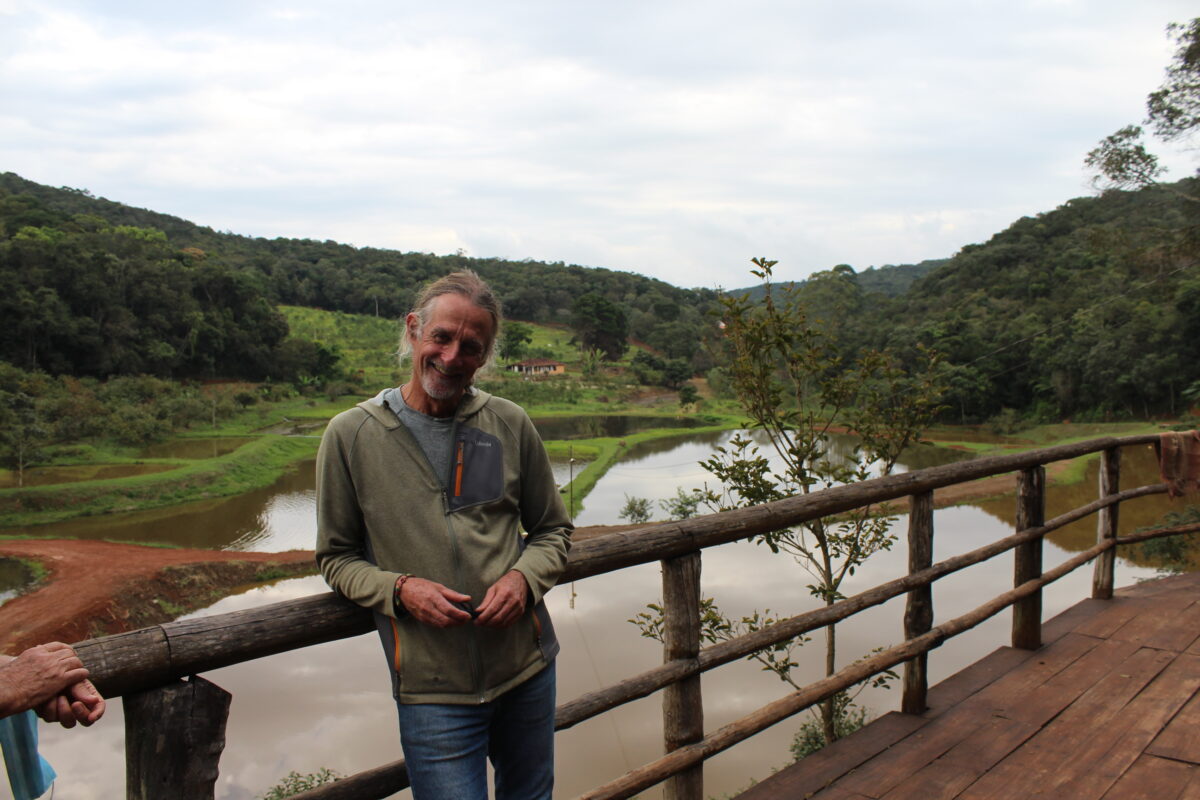
In São Bartolomeu, a town in the municipality of Ouro Preto, Ronald Guerra, an ecotourism entrepreneur, proposes a succession of small dams and reservoirs as a way of retaining water, feeding the water table and preventing erosion.
On his 120-hectare farm, half of which is recognized as a Private Natural Heritage Reserve –a private initiative conservation effort – he has 13 small dams and raises fish for his restaurant and sport fishing.
The son of a doctor from Belo Horizonte, he opted for rural life and agroecology from a young age. He was secretary of environment of Ouro Preto and today he is an activist in several watershed committees, non-governmental organizations and efforts for the promotion of local culture.
© Inter Press Service (2022) — All Rights ReservedOriginal source: Inter Press Service
Check out our Latest News and Follow us at Facebook
Original Source